As we discussed in Part One of “Precision Machine Alignment Critical to Fabric Performance, Sheet Formation & Water Removal”, the precision alignment of the components in the forming, pressing, and drying sections of a paper machine, can have a direct effect on fabric performance. Component misalignment can cause significant fabric issues such as fabric weaving, fabric slipping on driven components, trade seem skew and more, resulting in poor sheet formation and less than optimal water removal. In Part Two of this article, we discuss alignment tips and techniques for these particular sections and provide an overview of alignment tooling and technologies. You will also learn the benefits of properly aligned forming, pressing, and drying sections.
Alignment Tips & Techniques
It is important to understand the overall paper making process – continuous web from forming section to reel – in order to establish a paper machine alignment methodology that ensures precision alignment throughout the entire machine. 
In general, all machine components should be aligned level to earth and perpendicular to machine centerline. For an entirely new machine installation this may seem fairly straight forward – layout a straight line in the floor and set all equipment on centerline, level and square to that centerline. However, when existing equipment is in operation and inspection of and alignment of components is to take place, it is vital that proper methodologies are followed.
- An overall machine centerline survey should be performed and monuments installed in the operating aisle floor. These monuments will serve as an offset representation of the machine centerline. Then optical tooling or laser trackers can be utilized from wet end to dry end for documentation of equipment alignment conditions.
- Transitions should be established when aligning only one section of a machine at a time or during a rebuild effort. Proper transitions will allow for continuous sheet transition from one section to the next thereby avoiding sheet breaks.
- Forming Zone – Know original specifications/geometry or modified/expected dimensions for alignment. Be prepared to present this information to your alignment company so they can verify, assist with alignment and document.
- Press Section – During an outage, have the ability to nip rolls and if possible plan to have felts removed as felts can restrict lines of sight (LOS)
- Dryers – Plan for a cooling off period from shutdown to time to begin inspecting components. Radiant heat will affect optical LOS or laser beam from tracker. Again, it is best to plan on performing inspections when fabrics are removed as fabrics can restrict LOS and always had rather inspect off roll surface and not on fabric
- Documentation – You want your alignment data collected and documented in a formal report. This data will serve as history which may show patterns (areas that you struggle to maintain precision alignment) and recommendations on ways to correct and maintain alignment of components.
Alignment Tooling & Technologies
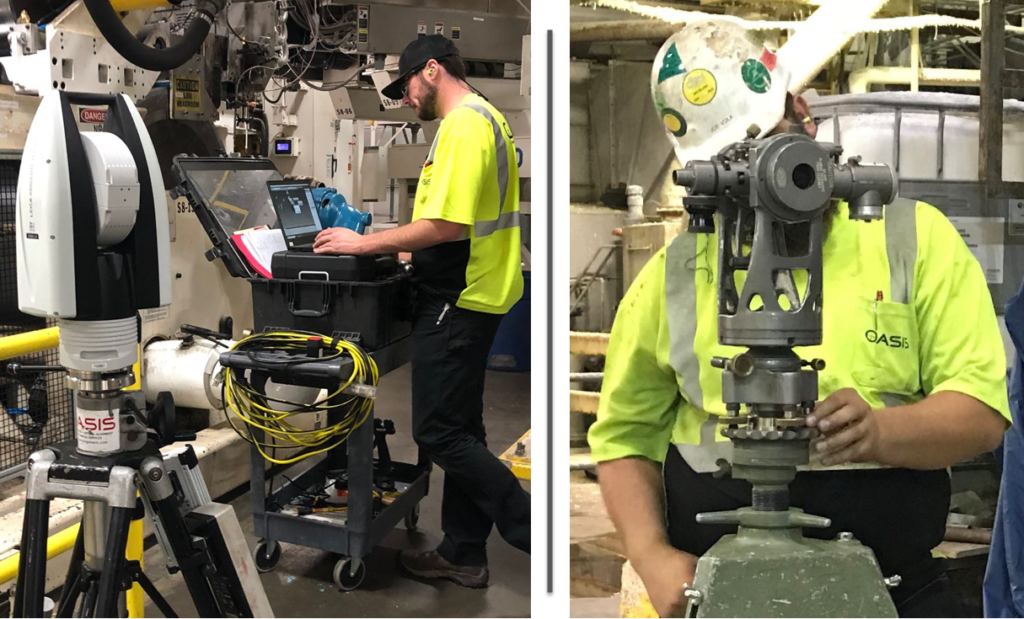
There are various techniques for alignment but many are out dated and few people know how to utilize those out dated techniques. The preferred techniques are utilization of optical alignment tooling and/or laser-based equipment, such as the laser tracker. Highly accurate optical tooling and laser trackers can measure to 0.001” and easily provide precision measurement standards and tolerances required by manufacturers.
Optical tooling and laser trackers use established reference points and allow for measurements to be obtained on all locations of equipment in both vertical and horizontal location and alignment positioning. In general, machine components are measured, end-to-end, to determine relative alignment conditions and corrections are made at mounting surfaces for precision alignment.
Proper use of precision measurement instruments will yield optimal alignment results. The measurement instrument though, is only as good as its operator. When properly trained, alignment engineers and field service technicians can obtain and document precision alignment data that validates the alignment of new and existing equipment.

Benefits of Precision Alignment
You gain time through:
Increased efficiency – improved fabric performance and sheet formation, and improved press performance and drying capabilities.
Less machine downtime – decreased sheet breaks and bearing, coupling, and gear failures and fabrics lasting their expected life cycle
Optimum production levels – Meet target number of tons per day; meet or exceed KPIs
High quality end product – improved product quality and less scrap, and satisfied customers
You can spend more time on what matters most: People. Quality. Productivity.
Be sure to check out Part One of this article and remember to Subscribe to our email list for this and more educational articles on precision measurement tooling and technologies, machine alignment methods, case studies and more.
If you would like to speak to an OASIS representative about quality or productivity issues you are having at your mill, we are available to help. Please Contact Us today!

